library(tidyverse)
churn<-readr::read_csv("Databel_Data.csv")
churn |>
head(10) |>
flextable::flextable()Introduction to Customer Churning
Comparing R and Powerbi DAX
- this blog aims to compare how things are done in R and Powerbi
Data Analysis Expressions (DAX) is a formula expression language used in Analysis Services, Power BI, and Power Pivot in Excel. DAX formulas include functions, operators, and values to perform advanced calculations and queries on data in related tables and columns in tabular data models.
- This article provides only a basic introduction to the most important concepts in DAX while comparing them to R
Data exploration
- before any analysis , it is mandatory to learn more about the rows in our data
- things like the
number of rows in our dataandduplicate columnsin our data are very important to understand
churn |>
summarise(`number of customers` = n(),
`distinct customers` = n_distinct(`Customer ID`))# A tibble: 1 × 2
`number of customers` `distinct customers`
<int> <int>
1 6687 6687OR
(`Number of Customers` <- count(churn))# A tibble: 1 × 1
n
<int>
1 6687- in powerbi our dataframe is
Databel - Dataand to index our data we use'Databel - Data'[variable]
to find the number of rows we use
COUNT()orCOUNTROWS()
Number of Customers = COUNT('Databel - Data'[Customer ID])to find the number of UNIQUE customers we use
DISTINCTCOUNT()orCOUNTROWS()
Number of Customers = DISTINCTCOUNT('Databel - Data'[Customer ID])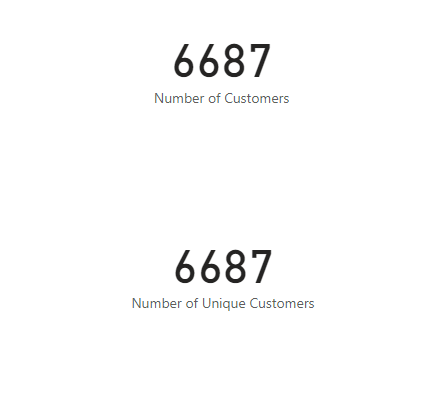
Data manipulation
IF STATEMENTS
in dplyr we use
ifelse()in conjuction withmutate()to create a new variable based on a certain condition or criteria
# A tibble: 6,687 × 30
churned `Customer ID` `Churn Label` Account Length (in months…¹ `Local Calls`
<dbl> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <dbl>
1 0 4444-BZPU No 1 3
2 0 5676-PTZX No 33 179
3 0 8532-ZEKQ No 44 82
4 0 1314-SMPJ No 10 47
5 0 2956-TXCJ No 62 184
6 0 9152-DEPY No 17 68
7 0 1958-SDSO No 57 428
8 0 8787-QZUC No 25 54
9 0 7768-OQJE No 70 171
10 0 7716-RHEB No 50 206
# ℹ 6,677 more rows
# ℹ abbreviated name: ¹`Account Length (in months)`
# ℹ 25 more variables: `Local Mins` <dbl>, `Intl Calls` <dbl>,
# `Intl Mins` <dbl>, `Intl Active` <chr>, `Intl Plan` <chr>,
# `Extra International Charges` <dbl>, `Customer Service Calls` <dbl>,
# `Avg Monthly GB Download` <dbl>, `Unlimited Data Plan` <chr>,
# `Extra Data Charges` <dbl>, State <chr>, `Phone Number` <chr>, …in
DAXwe useIF(), uses the same idea asR
Churned = IF('Databel - Data'[Churn Label]="Yes",1,0)
Calculate churn Rate
for that we first calculate the number of
customers that churned,
- in R we can sum over the
churnedcolumn since we know it contains Zeros and ones
(`Number of Churned Customers` = sum(churn$churned))[1] 1796- about
1796people churned
do it in
DAX, we usesum() or SUM()just like R
The only difference is we used $ in R
Number of Churned Customers = SUM('Databel - Data'[Churned])(`Churn Rate` = `Number of Churned Customers`/`Number of Customers`$n)* 100[1] 26.85808Churn Rate in PowerBi , just like in R we use
/to imply divide
Churn Rate = [Number of Churned Customers]/[Number of Customers]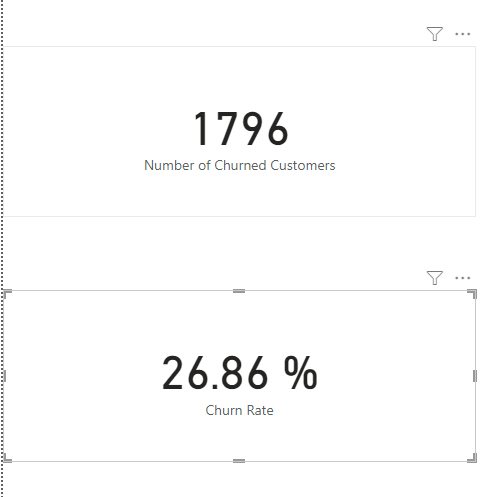
overally we get
26.86%churn rate
Lets determine the frequent reasaons for churning
in R we use ggplot2 package to plot our data
churn |>
na.omit() |>
group_by(`Churn Reason`) |>
summarise(n = n()) |>
ggplot(aes(x= fct_reorder(`Churn Reason`,n) , y= n))+
geom_col(fill="blue")+
coord_flip()+
ggthemes::theme_economist()+
labs(x="Churn Reason",y="number of customers")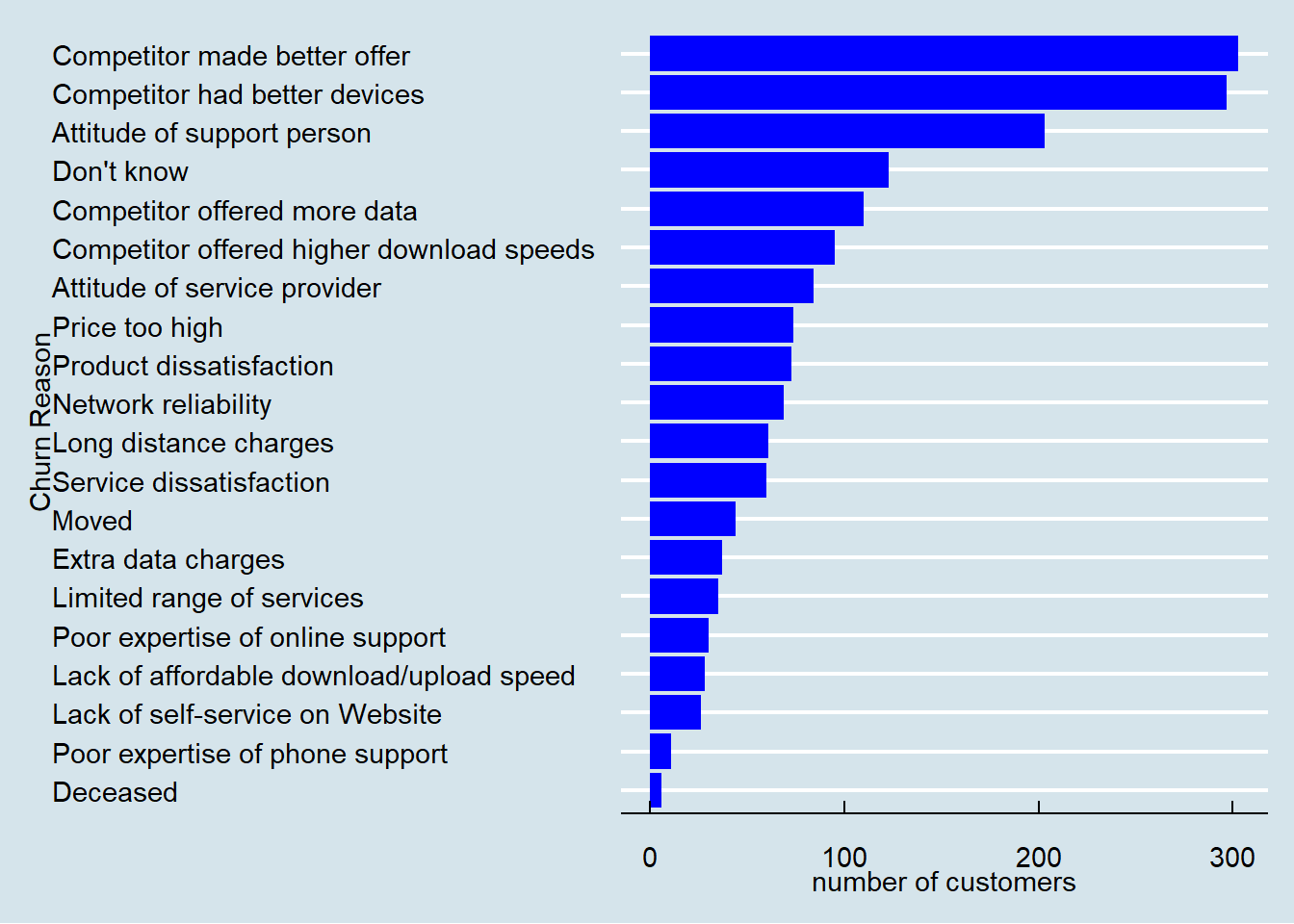
in Powerbi we simply selected a
clustered bar chart
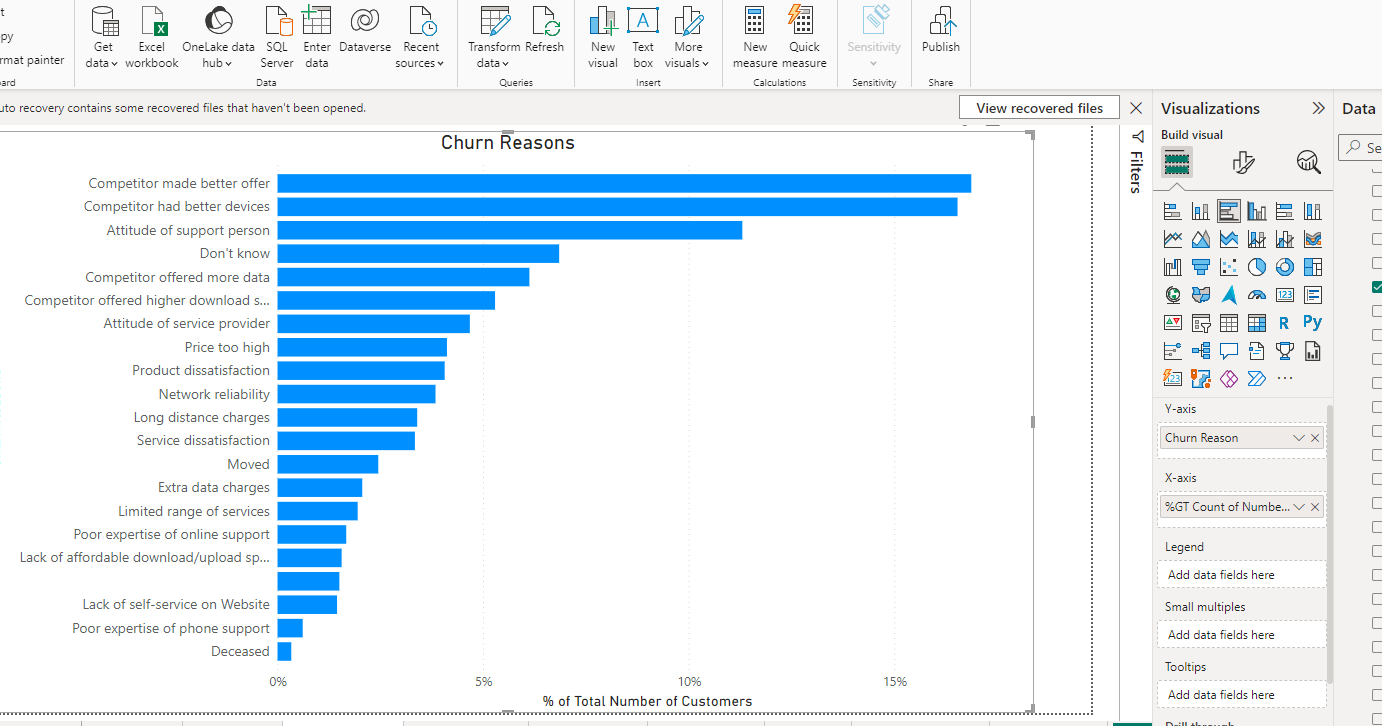
More advanced data manipulation
table(churn$`Contract Type`)
Month-to-Month One Year Two Year
3411 1479 1797 suppose we intend to have just
yearandMonthlycontract types , we can choose to bundle upOne yearandTwo Yearinto justYearcategory.
(churn<-churn |>
mutate(`Contract Category` = case_when(`Contract Type` =="One Year"~ "Yearly",
`Contract Type` =="Two Year"~ "Yearly",
`Contract Type` =="Month-to-Month"~ "Monthly")) |>
relocate(`Contract Category`))# A tibble: 6,687 × 31
`Contract Category` churned `Customer ID` `Churn Label`
<chr> <dbl> <chr> <chr>
1 Monthly 0 4444-BZPU No
2 Yearly 0 5676-PTZX No
3 Yearly 0 8532-ZEKQ No
4 Monthly 0 1314-SMPJ No
5 Yearly 0 2956-TXCJ No
6 Yearly 0 9152-DEPY No
7 Yearly 0 1958-SDSO No
8 Monthly 0 8787-QZUC No
9 Yearly 0 7768-OQJE No
10 Yearly 0 7716-RHEB No
# ℹ 6,677 more rows
# ℹ 27 more variables: `Account Length (in months)` <dbl>, `Local Calls` <dbl>,
# `Local Mins` <dbl>, `Intl Calls` <dbl>, `Intl Mins` <dbl>,
# `Intl Active` <chr>, `Intl Plan` <chr>,
# `Extra International Charges` <dbl>, `Customer Service Calls` <dbl>,
# `Avg Monthly GB Download` <dbl>, `Unlimited Data Plan` <chr>,
# `Extra Data Charges` <dbl>, State <chr>, `Phone Number` <chr>, …
SWITCH(<expression>, <value>, <result>[, <value>, <result>]…[, <else>])
Contract Category = SWITCH('Databel - Data'[Contract Type],
"One Year", "Yearly",
"Two Year", "Yearly",
"Monthly")
Churn Rates By state
In R we use the power of
mutateandsprintf()
churn |>
group_by(State) |>
summarise(`# of customers` = n(),
`# of churned customers` = sum(churned),
`Churn Rate` = sprintf("%.2f%%",`# of churned customers`/`# of customers`* 100)) |>
knitr::kable()| State | # of customers | # of churned customers | Churn Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| AK | 104 | 30 | 28.85% |
| AL | 161 | 46 | 28.57% |
| AR | 110 | 27 | 24.55% |
| AZ | 128 | 30 | 23.44% |
| CA | 68 | 43 | 63.24% |
| CO | 132 | 29 | 21.97% |
| CT | 148 | 38 | 25.68% |
| DC | 108 | 21 | 19.44% |
| DE | 122 | 37 | 30.33% |
| FL | 127 | 27 | 21.26% |
| GA | 108 | 25 | 23.15% |
| HI | 106 | 28 | 26.42% |
| IA | 90 | 24 | 26.67% |
| ID | 147 | 41 | 27.89% |
| IL | 116 | 33 | 28.45% |
| IN | 143 | 42 | 29.37% |
| KS | 141 | 36 | 25.53% |
| KY | 118 | 36 | 30.51% |
| LA | 103 | 25 | 24.27% |
| MA | 131 | 33 | 25.19% |
| MD | 140 | 46 | 32.86% |
| ME | 124 | 29 | 23.39% |
| MI | 146 | 40 | 27.40% |
| MN | 168 | 38 | 22.62% |
| MO | 127 | 36 | 28.35% |
| MS | 130 | 37 | 28.46% |
| MT | 137 | 43 | 31.39% |
| NC | 136 | 28 | 20.59% |
| ND | 124 | 31 | 25.00% |
| NE | 122 | 40 | 32.79% |
| NH | 112 | 36 | 32.14% |
| NJ | 137 | 37 | 27.01% |
| NM | 124 | 30 | 24.19% |
| NV | 132 | 36 | 27.27% |
| NY | 167 | 39 | 23.35% |
| OH | 158 | 55 | 34.81% |
| OK | 123 | 24 | 19.51% |
| OR | 156 | 48 | 30.77% |
| PA | 90 | 30 | 33.33% |
| RI | 131 | 33 | 25.19% |
| SC | 120 | 36 | 30.00% |
| SD | 120 | 27 | 22.50% |
| TN | 106 | 24 | 22.64% |
| TX | 145 | 42 | 28.97% |
| UT | 144 | 36 | 25.00% |
| VA | 155 | 42 | 27.10% |
| VT | 147 | 39 | 26.53% |
| WA | 132 | 29 | 21.97% |
| WI | 156 | 39 | 25.00% |
| WV | 213 | 57 | 26.76% |
| WY | 154 | 38 | 24.68% |
in powerbi we use a
tableto summarise our data just by clicking
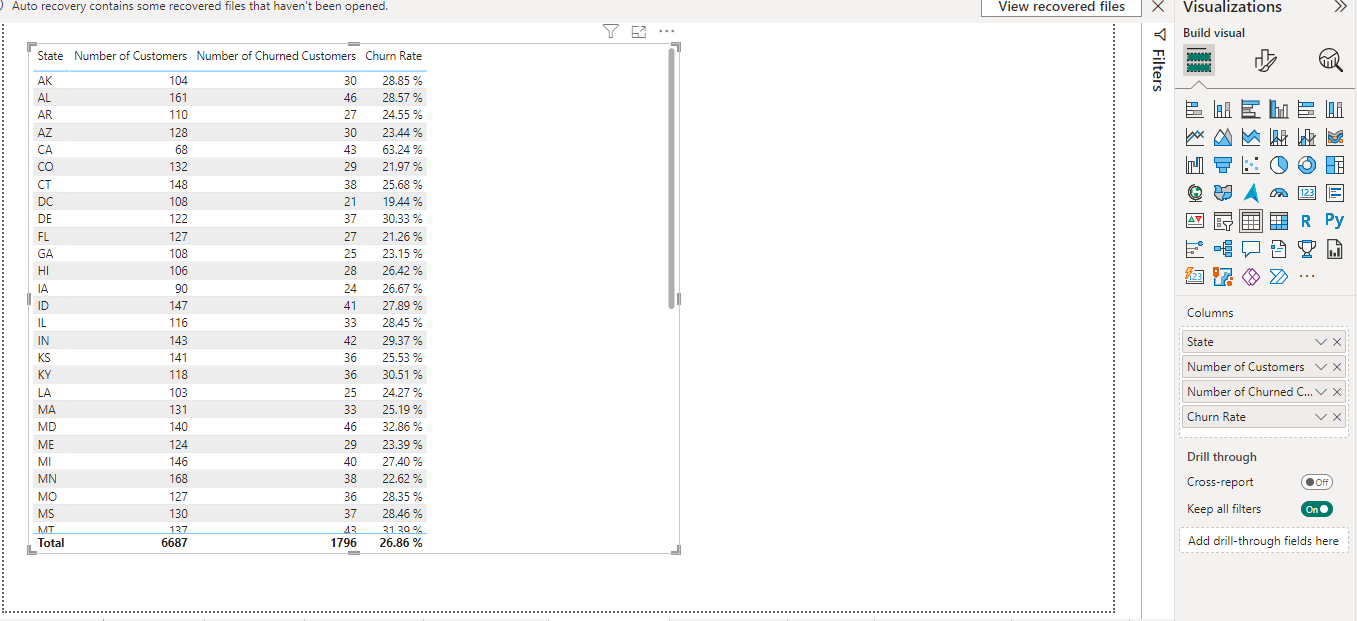
Filtering
- filtering is a common pocedure in data science
here is how we do it in R as compared to DAX
- In R we use
filter() then summarise()to get the mean for only a certain category
CALCULATE(<expression>[, <filter1> [, <filter2> [, …]]])
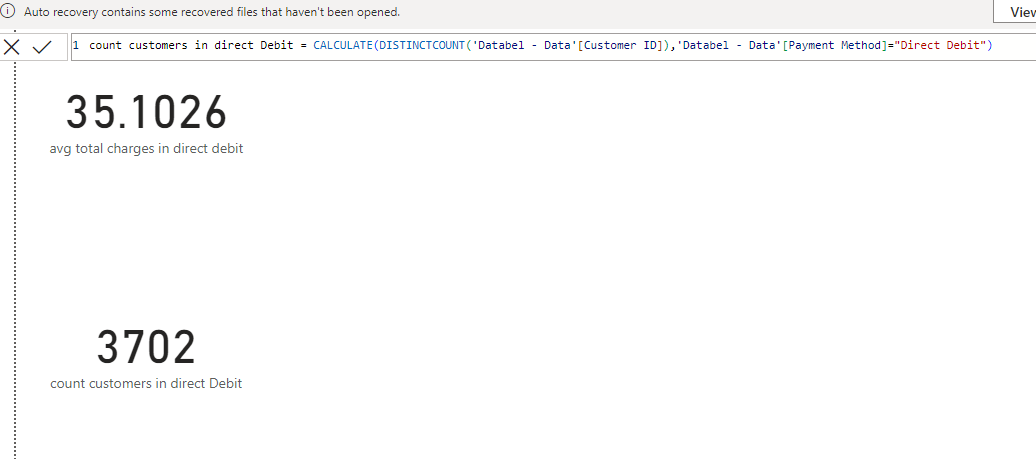
avg total charges in direct debit = CALCULATE(AVERAGE('Databel - Data'[Monthly Charge]),
'Databel - Data'[Payment Method]="Direct Debit")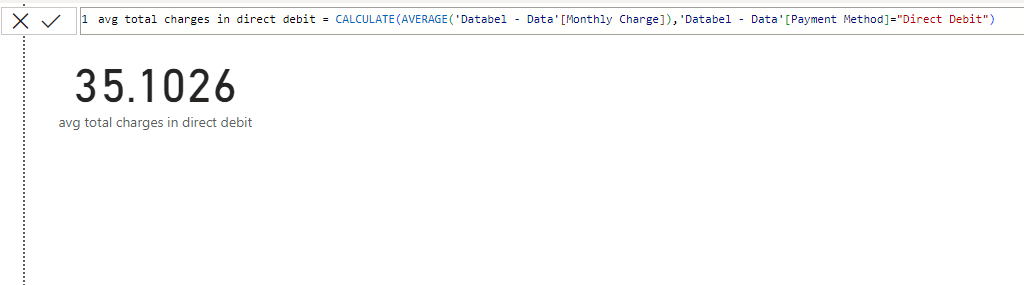
churn |>
filter(`Payment Method` == "Direct Debit") |>
summarise(`count customers in direct Debit` = n_distinct(`Customer ID`))# A tibble: 1 × 1
`count customers in direct Debit`
<int>
1 3702avg total charges in direct debit = CALCULATE(DISTINCTCOUNT('Databel - Data'[CUSTOMER ID]),
'Databel - Data'[Payment Method]="Direct Debit")