sales<-tribble(~ year , ~country , ~product , ~profit ,~Own ,~Time,
2000 , "Finland", "Computer" , 1500 ,"Y" ,"D",
2000 , "Finland" ,"Phone" , 100 ,"Y" ,"D",
2001 , "Finland" ,"Phone" , 10 ,"N" ,"D",
2000 , "India" ,"Calculator" , 75 ,"Y" ,"E",
2000 , "India" ,"Calculator" , 75 ,"N" ,"E",
2000 , "India" ,"Computer" , 1200 ,"N" ,"E",
2000 , "USA" , "Calculator", 75 ,"Y" ,"E",
2000 , "USA" , "Computer" , 1500 ,"N" ,"E",
2001 , "USA" ,"Calculator" , 50 ,"Y" ,"E",
2001 , "USA" ,"Computer" , 1500 ,"Y" ,"E",
2001 , "USA" ,"Computer" , 1200 ,"Y" ,"D",
2001 , "USA" , "TV" , 150 ,"Y" ,"D",
2001 , "USA" , "TV" , 100 ,"Y" ,"D")
sales
#> # A tibble: 13 × 6
#> year country product profit Own Time
#> <dbl> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <chr> <chr>
#> 1 2000 Finland Computer 1500 Y D
#> 2 2000 Finland Phone 100 Y D
#> 3 2001 Finland Phone 10 N D
#> 4 2000 India Calculator 75 Y E
#> 5 2000 India Calculator 75 N E
#> 6 2000 India Computer 1200 N E
#> 7 2000 USA Calculator 75 Y E
#> 8 2000 USA Computer 1500 N E
#> 9 2001 USA Calculator 50 Y E
#> 10 2001 USA Computer 1500 Y E
#> 11 2001 USA Computer 1200 Y D
#> 12 2001 USA TV 150 Y D
#> 13 2001 USA TV 100 Y DSQL and R compared
Comparing R and SQL
Loading data
The Notebook is divided into tabbed sections as seen below.
loading data in R
loading data in SQL
CREATE TABLE profits (sales_id INT PRIMARY KEY,
year INT,
country VARCHAR(50),
product VARCHAR(50),
profit DECIMAL(10,2)
);
INSERT INTO profits VALUES (1,2000 , "Finland", "Computer" , 1500 ),
(2,2000 , "Finland" ,"Phone" , 100 ),
(3,2001 , "Finland" ,"Phone" , 10),
(4,2000 , "India" ,"Calculator" , 75),
(5,2000 , "India" ,"Calculator" , 75),
(6,2000 , "India" ,"Computer" , 1200),
(7,2000 , "USA" , "Calculator", 75),
(8,2000 , "USA" , "Computer" , 1500),
(9,2001 , "USA" ,"Calculator" , 50),
(10,2001 , "USA" ,"Computer" , 1500),
(11,2001 , "USA" ,"Computer" , 1200),
(12,2001 , "USA" , "TV" , 150),
(13,2001 , "USA" , "TV" , 100);
#> # A tibble: 13 × 6
#> year country product profit Own Time
#> <dbl> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <chr> <chr>
#> 1 2000 Finland Computer 1500 Y D
#> 2 2000 Finland Phone 100 Y D
#> 3 2001 Finland Phone 10 N D
#> 4 2000 India Calculator 75 Y E
#> 5 2000 India Calculator 75 N E
#> 6 2000 India Computer 1200 N E
#> 7 2000 USA Calculator 75 Y E
#> 8 2000 USA Computer 1500 N E
#> 9 2001 USA Calculator 50 Y E
#> 10 2001 USA Computer 1500 Y E
#> 11 2001 USA Computer 1200 Y D
#> 12 2001 USA TV 150 Y D
#> 13 2001 USA TV 100 Y DSelecting columns
selecting columns in R
sales |> select(everything())
#> # A tibble: 13 × 6
#> year country product profit Own Time
#> <dbl> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <chr> <chr>
#> 1 2000 Finland Computer 1500 Y D
#> 2 2000 Finland Phone 100 Y D
#> 3 2001 Finland Phone 10 N D
#> 4 2000 India Calculator 75 Y E
#> 5 2000 India Calculator 75 N E
#> 6 2000 India Computer 1200 N E
#> 7 2000 USA Calculator 75 Y E
#> 8 2000 USA Computer 1500 N E
#> 9 2001 USA Calculator 50 Y E
#> 10 2001 USA Computer 1500 Y E
#> 11 2001 USA Computer 1200 Y D
#> 12 2001 USA TV 150 Y D
#> 13 2001 USA TV 100 Y Dselecting all columns in SQL
SELECT *
FROM sales;| year | country | product | profit | Own | Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 | Finland | Computer | 1500 | Y | D |
| 2000 | Finland | Phone | 100 | Y | D |
| 2001 | Finland | Phone | 10 | N | D |
| 2000 | India | Calculator | 75 | Y | E |
| 2000 | India | Calculator | 75 | N | E |
| 2000 | India | Computer | 1200 | N | E |
| 2000 | USA | Calculator | 75 | Y | E |
| 2000 | USA | Computer | 1500 | N | E |
| 2001 | USA | Calculator | 50 | Y | E |
| 2001 | USA | Computer | 1500 | Y | E |
Select a subset of columns
selecting subset columns in R
sales |>
select(year,country,product)
#> # A tibble: 13 × 3
#> year country product
#> <dbl> <chr> <chr>
#> 1 2000 Finland Computer
#> 2 2000 Finland Phone
#> 3 2001 Finland Phone
#> 4 2000 India Calculator
#> 5 2000 India Calculator
#> 6 2000 India Computer
#> 7 2000 USA Calculator
#> 8 2000 USA Computer
#> 9 2001 USA Calculator
#> 10 2001 USA Computer
#> 11 2001 USA Computer
#> 12 2001 USA TV
#> 13 2001 USA TVselecting subset columns in SQL
SELECT year,country,product
FROM sales;| year | country | product |
|---|---|---|
| 2000 | Finland | Computer |
| 2000 | Finland | Phone |
| 2001 | Finland | Phone |
| 2000 | India | Calculator |
| 2000 | India | Calculator |
| 2000 | India | Computer |
| 2000 | USA | Calculator |
| 2000 | USA | Computer |
| 2001 | USA | Calculator |
| 2001 | USA | Computer |
filtering data
Filtering data in R
sales |>
filter(product=="Computer")
#> # A tibble: 5 × 6
#> year country product profit Own Time
#> <dbl> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <chr> <chr>
#> 1 2000 Finland Computer 1500 Y D
#> 2 2000 India Computer 1200 N E
#> 3 2000 USA Computer 1500 N E
#> 4 2001 USA Computer 1500 Y E
#> 5 2001 USA Computer 1200 Y DFiltering data in SQL
SELECT *
FROM sales
WHERE product='Computer';| year | country | product | profit | Own | Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 | Finland | Computer | 1500 | Y | D |
| 2000 | India | Computer | 1200 | N | E |
| 2000 | USA | Computer | 1500 | N | E |
| 2001 | USA | Computer | 1500 | Y | E |
| 2001 | USA | Computer | 1200 | Y | D |
filtering with AND
Filtering data in R
sales |>
filter(product=="Computer" & year=="2001")
#> # A tibble: 2 × 6
#> year country product profit Own Time
#> <dbl> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <chr> <chr>
#> 1 2001 USA Computer 1500 Y E
#> 2 2001 USA Computer 1200 Y DFiltering data in SQL
SELECT *
FROM sales
WHERE product='Computer' AND year='2001';| year | country | product | profit | Own | Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2001 | USA | Computer | 1500 | Y | E |
| 2001 | USA | Computer | 1200 | Y | D |
filtering with OR
Filtering data in R
sales |>
filter(product=="Computer"| country=="USA")
#> # A tibble: 9 × 6
#> year country product profit Own Time
#> <dbl> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <chr> <chr>
#> 1 2000 Finland Computer 1500 Y D
#> 2 2000 India Computer 1200 N E
#> 3 2000 USA Calculator 75 Y E
#> 4 2000 USA Computer 1500 N E
#> 5 2001 USA Calculator 50 Y E
#> 6 2001 USA Computer 1500 Y E
#> 7 2001 USA Computer 1200 Y D
#> 8 2001 USA TV 150 Y D
#> 9 2001 USA TV 100 Y DFiltering data in SQL
SELECT *
FROM sales
WHERE product='Computer' OR country='USA';| year | country | product | profit | Own | Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 | Finland | Computer | 1500 | Y | D |
| 2000 | India | Computer | 1200 | N | E |
| 2000 | USA | Calculator | 75 | Y | E |
| 2000 | USA | Computer | 1500 | N | E |
| 2001 | USA | Calculator | 50 | Y | E |
| 2001 | USA | Computer | 1500 | Y | E |
| 2001 | USA | Computer | 1200 | Y | D |
| 2001 | USA | TV | 150 | Y | D |
| 2001 | USA | TV | 100 | Y | D |
filtering with BETWEEN
Filtering data in R
sales |>
filter(between(profit,0,100))
#> # A tibble: 7 × 6
#> year country product profit Own Time
#> <dbl> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <chr> <chr>
#> 1 2000 Finland Phone 100 Y D
#> 2 2001 Finland Phone 10 N D
#> 3 2000 India Calculator 75 Y E
#> 4 2000 India Calculator 75 N E
#> 5 2000 USA Calculator 75 Y E
#> 6 2001 USA Calculator 50 Y E
#> 7 2001 USA TV 100 Y DFiltering data in SQL
SELECT *
FROM sales
WHERE profit BETWEEN 0 AND 100;| year | country | product | profit | Own | Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 | Finland | Phone | 100 | Y | D |
| 2001 | Finland | Phone | 10 | N | D |
| 2000 | India | Calculator | 75 | Y | E |
| 2000 | India | Calculator | 75 | N | E |
| 2000 | USA | Calculator | 75 | Y | E |
| 2001 | USA | Calculator | 50 | Y | E |
| 2001 | USA | TV | 100 | Y | D |
Arranging data
Arranging data in R
sales |>
arrange(profit)
#> # A tibble: 13 × 6
#> year country product profit Own Time
#> <dbl> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <chr> <chr>
#> 1 2001 Finland Phone 10 N D
#> 2 2001 USA Calculator 50 Y E
#> 3 2000 India Calculator 75 Y E
#> 4 2000 India Calculator 75 N E
#> 5 2000 USA Calculator 75 Y E
#> 6 2000 Finland Phone 100 Y D
#> 7 2001 USA TV 100 Y D
#> 8 2001 USA TV 150 Y D
#> 9 2000 India Computer 1200 N E
#> 10 2001 USA Computer 1200 Y D
#> 11 2000 Finland Computer 1500 Y D
#> 12 2000 USA Computer 1500 N E
#> 13 2001 USA Computer 1500 Y EArranging data in SQL
SELECT *
FROM sales
ORDER BY profit;| year | country | product | profit | Own | Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2001 | Finland | Phone | 10 | N | D |
| 2001 | USA | Calculator | 50 | Y | E |
| 2000 | India | Calculator | 75 | Y | E |
| 2000 | India | Calculator | 75 | N | E |
| 2000 | USA | Calculator | 75 | Y | E |
| 2000 | Finland | Phone | 100 | Y | D |
| 2001 | USA | TV | 100 | Y | D |
| 2001 | USA | TV | 150 | Y | D |
| 2000 | India | Computer | 1200 | N | E |
| 2001 | USA | Computer | 1200 | Y | D |
Arranging data in DESC order
arranging data in R
sales |>
arrange(desc(profit))
#> # A tibble: 13 × 6
#> year country product profit Own Time
#> <dbl> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <chr> <chr>
#> 1 2000 Finland Computer 1500 Y D
#> 2 2000 USA Computer 1500 N E
#> 3 2001 USA Computer 1500 Y E
#> 4 2000 India Computer 1200 N E
#> 5 2001 USA Computer 1200 Y D
#> 6 2001 USA TV 150 Y D
#> 7 2000 Finland Phone 100 Y D
#> 8 2001 USA TV 100 Y D
#> 9 2000 India Calculator 75 Y E
#> 10 2000 India Calculator 75 N E
#> 11 2000 USA Calculator 75 Y E
#> 12 2001 USA Calculator 50 Y E
#> 13 2001 Finland Phone 10 N Darranging data in SQL
SELECT *
FROM sales
ORDER BY profit DESC;| year | country | product | profit | Own | Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 | Finland | Computer | 1500 | Y | D |
| 2000 | USA | Computer | 1500 | N | E |
| 2001 | USA | Computer | 1500 | Y | E |
| 2000 | India | Computer | 1200 | N | E |
| 2001 | USA | Computer | 1200 | Y | D |
| 2001 | USA | TV | 150 | Y | D |
| 2000 | Finland | Phone | 100 | Y | D |
| 2001 | USA | TV | 100 | Y | D |
| 2000 | India | Calculator | 75 | Y | E |
| 2000 | India | Calculator | 75 | N | E |
Mutating new columns
Mutating new columns in R
sales |>
mutate(profit=profit/1000)
#> # A tibble: 13 × 6
#> year country product profit Own Time
#> <dbl> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <chr> <chr>
#> 1 2000 Finland Computer 1.5 Y D
#> 2 2000 Finland Phone 0.1 Y D
#> 3 2001 Finland Phone 0.01 N D
#> 4 2000 India Calculator 0.075 Y E
#> 5 2000 India Calculator 0.075 N E
#> 6 2000 India Computer 1.2 N E
#> 7 2000 USA Calculator 0.075 Y E
#> 8 2000 USA Computer 1.5 N E
#> 9 2001 USA Calculator 0.05 Y E
#> 10 2001 USA Computer 1.5 Y E
#> 11 2001 USA Computer 1.2 Y D
#> 12 2001 USA TV 0.15 Y D
#> 13 2001 USA TV 0.1 Y DMutating new columns in SQL
SELECT profit/1000 AS profit,*
FROM sales;| profit | year | country | product | profit | Own | Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.500 | 2000 | Finland | Computer | 1500 | Y | D |
| 0.100 | 2000 | Finland | Phone | 100 | Y | D |
| 0.010 | 2001 | Finland | Phone | 10 | N | D |
| 0.075 | 2000 | India | Calculator | 75 | Y | E |
| 0.075 | 2000 | India | Calculator | 75 | N | E |
| 1.200 | 2000 | India | Computer | 1200 | N | E |
| 0.075 | 2000 | USA | Calculator | 75 | Y | E |
| 1.500 | 2000 | USA | Computer | 1500 | N | E |
| 0.050 | 2001 | USA | Calculator | 50 | Y | E |
| 1.500 | 2001 | USA | Computer | 1500 | Y | E |
Summarizing data
Summarizing data in R
sales |>
summarize(mean_profit=mean(profit),
count = n())
#> # A tibble: 1 × 2
#> mean_profit count
#> <dbl> <int>
#> 1 580. 13Summarizing data in SQL
SELECT AVG(profit) AS mean_profit,
COUNT(*) AS count
FROM sales;| mean_profit | count |
|---|---|
| 579.6154 | 13 |
Grouping and Summarizing data
Grouping and Summarizing data in R
sales |>
group_by(year) |>
summarize(mean_profit=mean(profit),
count = n())
#> # A tibble: 2 × 3
#> year mean_profit count
#> <dbl> <dbl> <int>
#> 1 2000 646. 7
#> 2 2001 502. 6Grouping and Summarizing data in SQL
SELECT year,
AVG(profit) AS mean_profit,
COUNT(*) AS count
FROM sales
GROUP BY year;| year | mean_profit | count |
|---|---|---|
| 2000 | 646.4286 | 7 |
| 2001 | 501.6667 | 6 |
data for joins
generally the following step show how a join is done in SQL
-
SELECTt1.comon_column1,t1.common_column2,… -
FROMtable1ASt1 -
<type> JOINtable2ASt2 -
ONt1.common_unique_column = t2.common_unique_column;
data for joins in R
join_df1
#> A B C
#> 1 red 2 3
#> 2 orange 4 6
#> 3 yellow 8 9
#> 4 green 0 0
#> 5 indigo 3 3
#> 6 blue 1 1
#> 7 purple 5 5
#> 8 white 8 2join_df2
#> A D
#> 1 red 3
#> 2 orange 5
#> 3 yellow 7
#> 4 green 1
#> 5 indigo 3
#> 6 blue 6
#> 7 pink 9data for joins in SQL
SELECT *
FROM join_df1;| A | B | C |
|---|---|---|
| red | 2 | 3 |
| orange | 4 | 6 |
| yellow | 8 | 9 |
| green | 0 | 0 |
| indigo | 3 | 3 |
| blue | 1 | 1 |
| purple | 5 | 5 |
| white | 8 | 2 |
SELECT *
FROM join_df2;| A | D |
|---|---|
| red | 3 |
| orange | 5 |
| yellow | 7 |
| green | 1 |
| indigo | 3 |
| blue | 6 |
| pink | 9 |
inner join
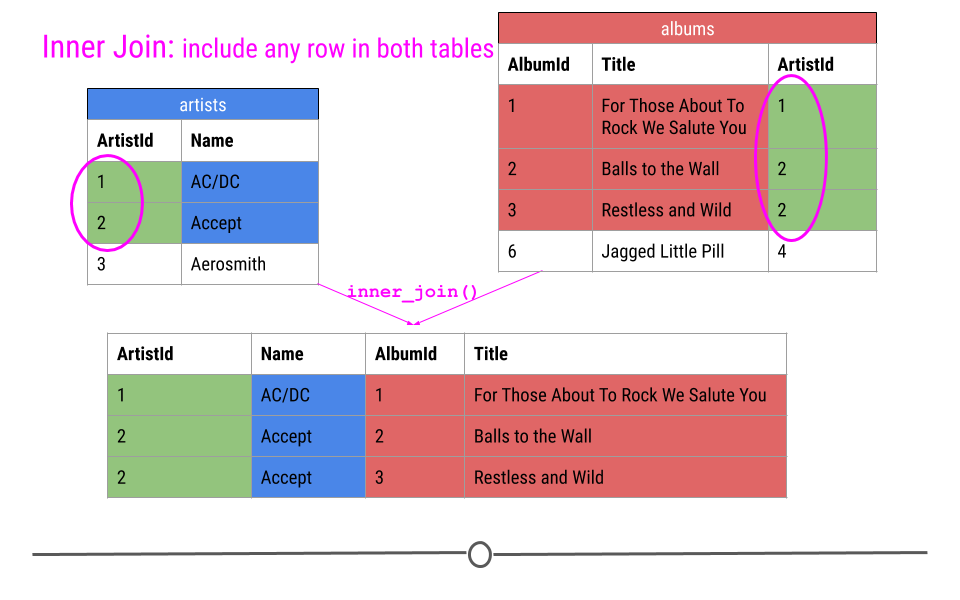
inner join in R
join_df1 |>
inner_join(join_df2, by = "A")
#> A B C D
#> 1 red 2 3 3
#> 2 orange 4 6 5
#> 3 yellow 8 9 7
#> 4 green 0 0 1
#> 5 indigo 3 3 3
#> 6 blue 1 1 6inner join in SQL
SELECT *
FROM join_df1 AS j1
INNER JOIN join_df2 AS j2
ON j1.A=j2.A;| A | B | C | A | D |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| red | 2 | 3 | red | 3 |
| orange | 4 | 6 | orange | 5 |
| yellow | 8 | 9 | yellow | 7 |
| green | 0 | 0 | green | 1 |
| indigo | 3 | 3 | indigo | 3 |
| blue | 1 | 1 | blue | 6 |
left join
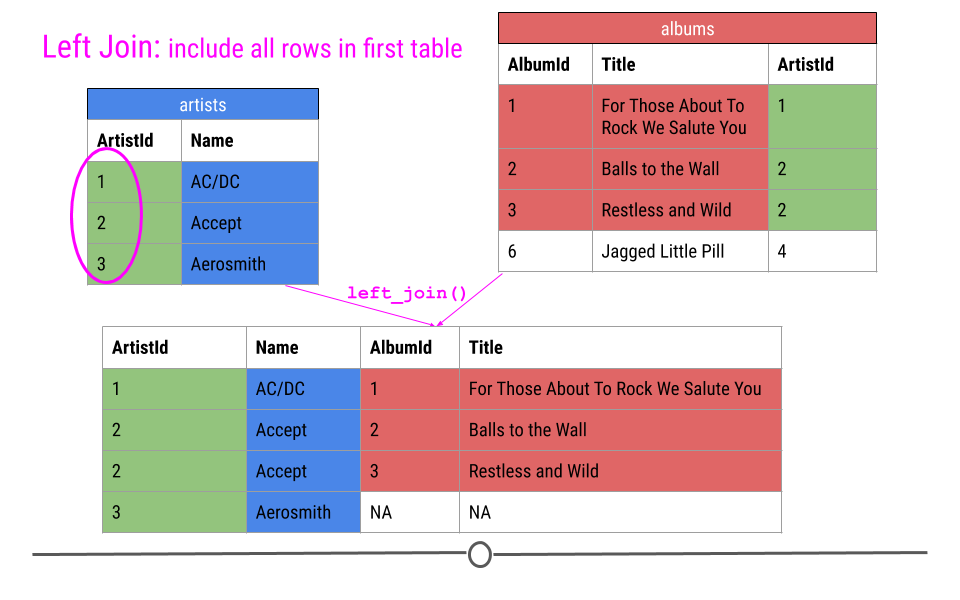
left join in R
join_df1 |>
left_join(join_df2, by = "A")
#> A B C D
#> 1 red 2 3 3
#> 2 orange 4 6 5
#> 3 yellow 8 9 7
#> 4 green 0 0 1
#> 5 indigo 3 3 3
#> 6 blue 1 1 6
#> 7 purple 5 5 NA
#> 8 white 8 2 NAleft join in SQL
SELECT j1.A,B,C,D
FROM join_df1 AS j1
LEFT JOIN join_df2 AS j2
ON j1.A=j2.A| A | B | C | D |
|---|---|---|---|
| red | 2 | 3 | 3 |
| orange | 4 | 6 | 5 |
| yellow | 8 | 9 | 7 |
| green | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| indigo | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| blue | 1 | 1 | 6 |
| purple | 5 | 5 | NA |
| white | 8 | 2 | NA |
Right join
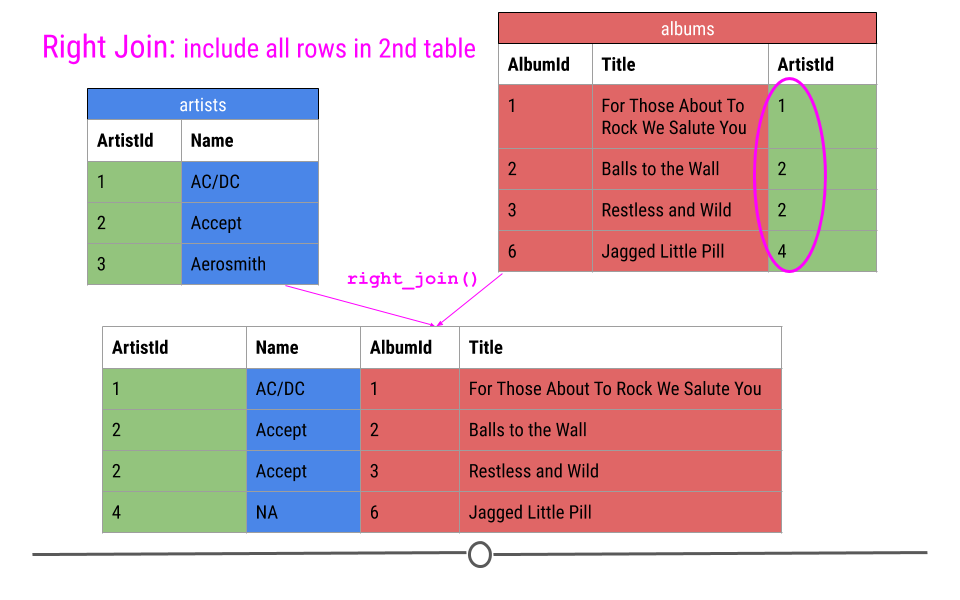
Right join in R
join_df1 |>
right_join(join_df2, by = "A")
#> A B C D
#> 1 red 2 3 3
#> 2 orange 4 6 5
#> 3 yellow 8 9 7
#> 4 green 0 0 1
#> 5 indigo 3 3 3
#> 6 blue 1 1 6
#> 7 pink NA NA 9Right join in SQL
SELECT j2.A,B,C,D
FROM join_df1 AS j1
RIGHT JOIN join_df2 AS j2
ON j1.A=j2.A| A | B | C | D |
|---|---|---|---|
| red | 2 | 3 | 3 |
| orange | 4 | 6 | 5 |
| yellow | 8 | 9 | 7 |
| green | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| indigo | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| blue | 1 | 1 | 6 |
| pink | NA | NA | 9 |
Full join
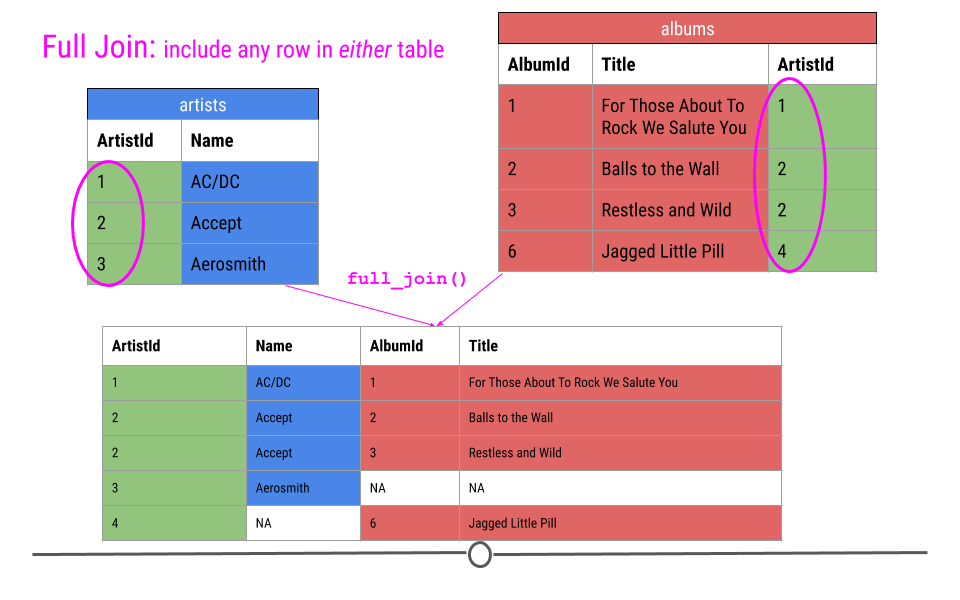
full join in R
join_df1 |>
full_join(join_df2, by = "A")
#> A B C D
#> 1 red 2 3 3
#> 2 orange 4 6 5
#> 3 yellow 8 9 7
#> 4 green 0 0 1
#> 5 indigo 3 3 3
#> 6 blue 1 1 6
#> 7 purple 5 5 NA
#> 8 white 8 2 NA
#> 9 pink NA NA 9full join in SQL
SELECT j1.A,B,C,D
FROM join_df1 AS j1
FULL JOIN join_df2 AS j2
ON j1.A=j2.A| A | B | C | D |
|---|---|---|---|
| red | 2 | 3 | 3 |
| orange | 4 | 6 | 5 |
| yellow | 8 | 9 | 7 |
| green | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| indigo | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| blue | 1 | 1 | 6 |
| purple | 5 | 5 | NA |
| white | 8 | 2 | NA |
| NA | NA | NA | 9 |